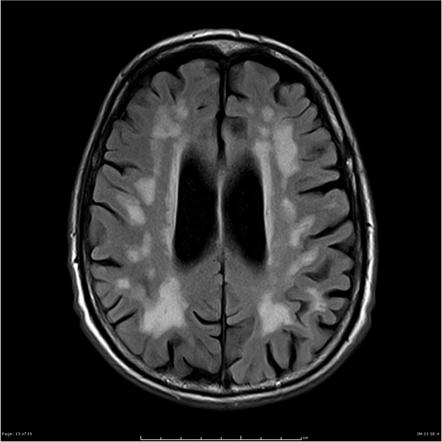
Moderate Chronic Small Vessel Ischemic Disease
Moderate chronic small vessel ischemic disease. These conditions include stroke cerebral hemorrhage and. Severe or prolonged ischemia can cause the tissue that is fed by the small vessels to die because of a lack of oxygen. Cerebral small vessel disease SVD includes white matter lesions WML and lacunar infarcts and is a frequent finding on computer tomography CT and magnetic resonance imaging MRI scans of elderly people 1.
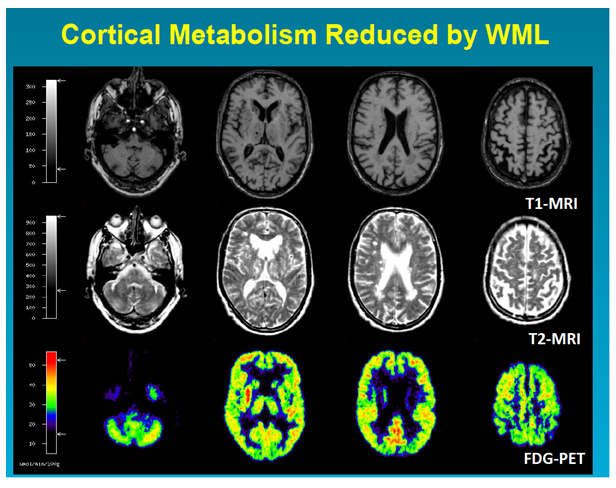
It is associated with vascular risk factors such as hypertension atherosclerosis diabetes mellitus and atrial fibrillation 2 4. Because most brain tissue appears white on MRIs these abnormalities were historically referred to as white matter changes. Ischemic cerebral small-vessel disease accounts for a third of acute cerebral ischemic events and contributes to the development of cognitive decline and dementia.
Microvascular ischemic disease describes conditions that affect the small blood vessels in the brain. Moderate chronic small vessel ischemic changes applies to certain areas of brain where there was deficient blood supply through small vessels rendering the tissues ischemic and degenerated. Clinical Information A disorder characterized by a decrease or absence of blood supply to the brain caused by obstruction thrombosis or embolism of an artery resulting in neurological damage.
The changes affect arterioles capillaries and small veins supplying the white matter and deep structures of the brain. Diminished or absent blood supply to the brain caused by obstruction thrombosis or embolism of an artery resulting in neurologic damage. This is a slow process and is seen in diabetics hypertensives or in advanced aging.
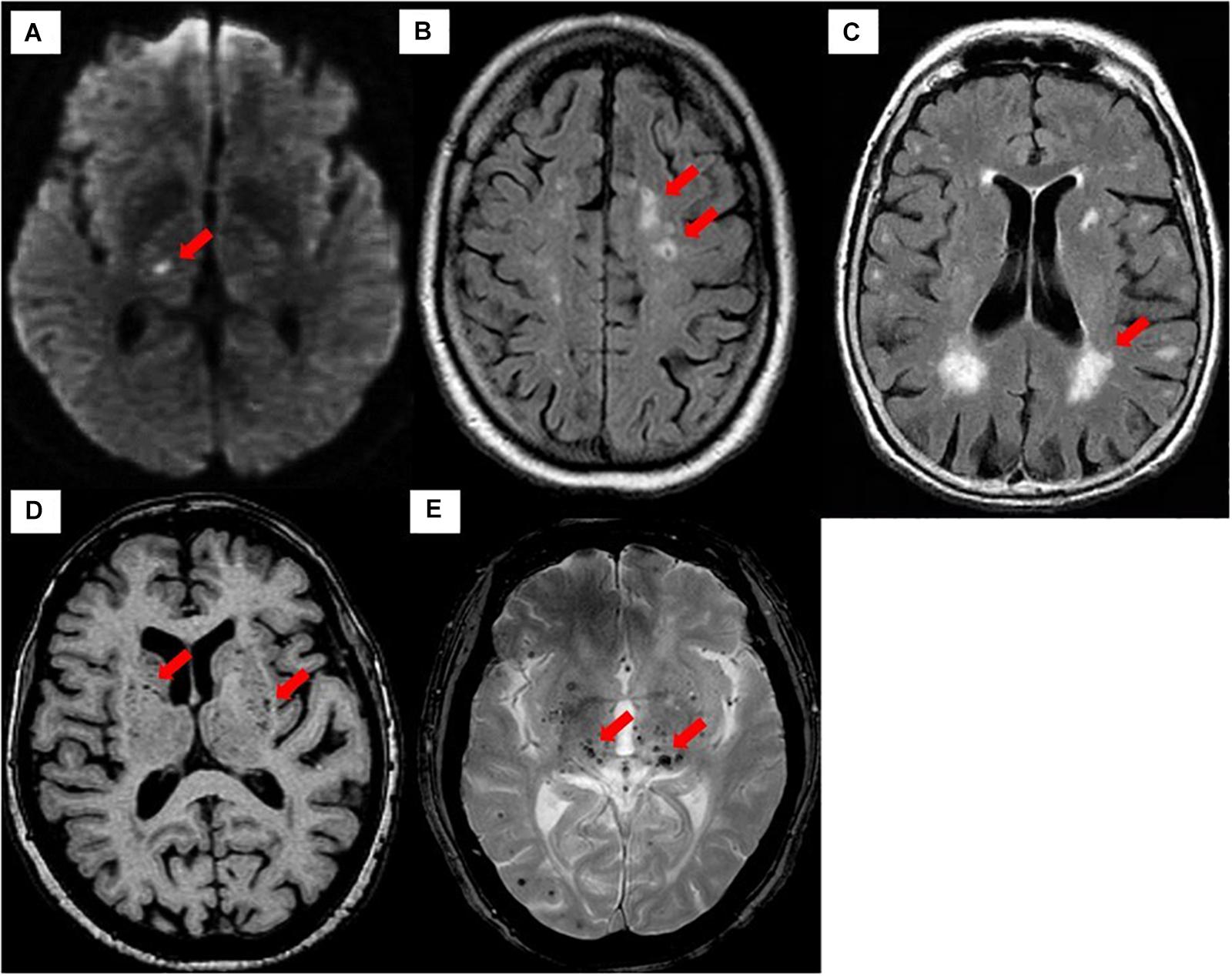
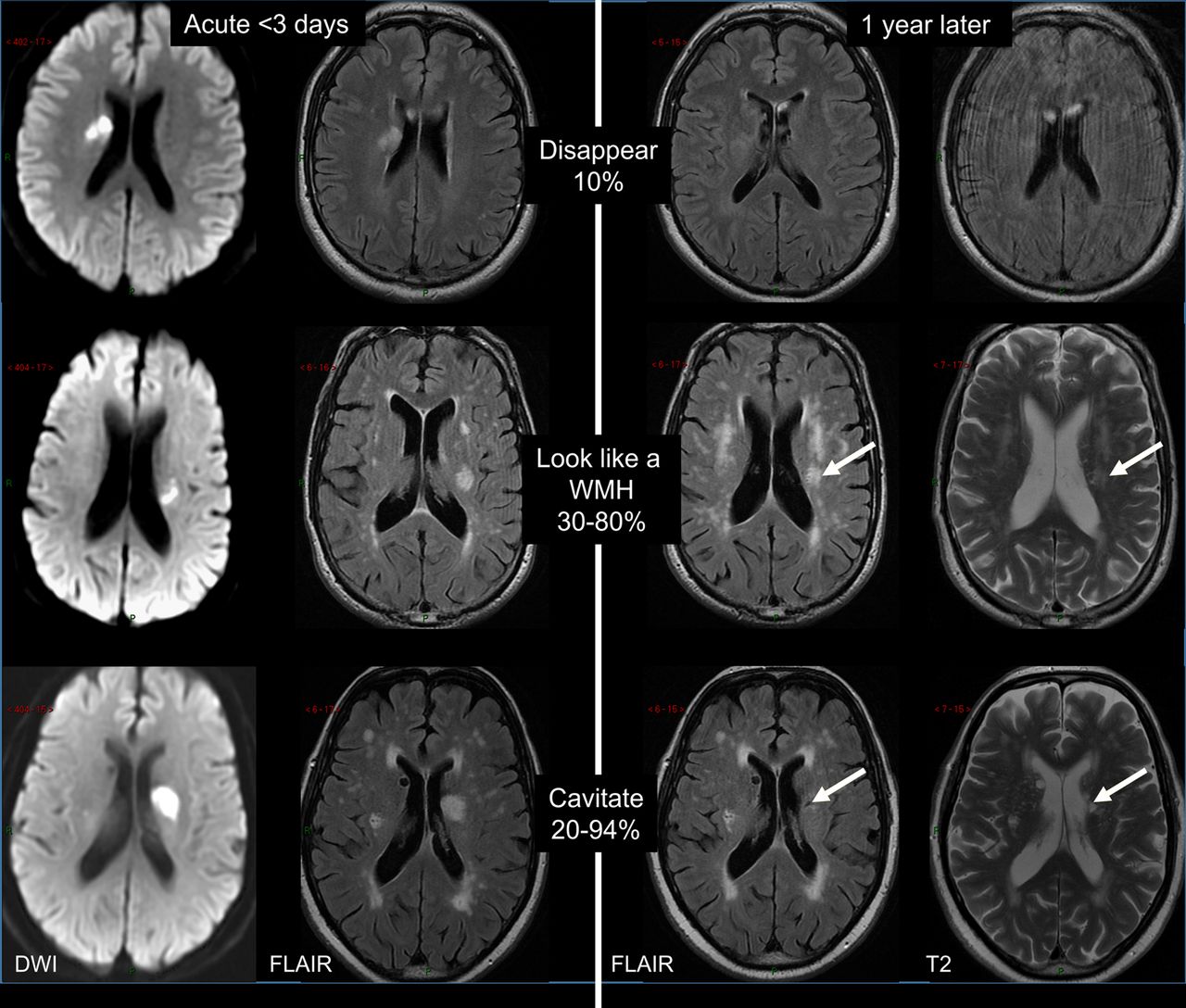
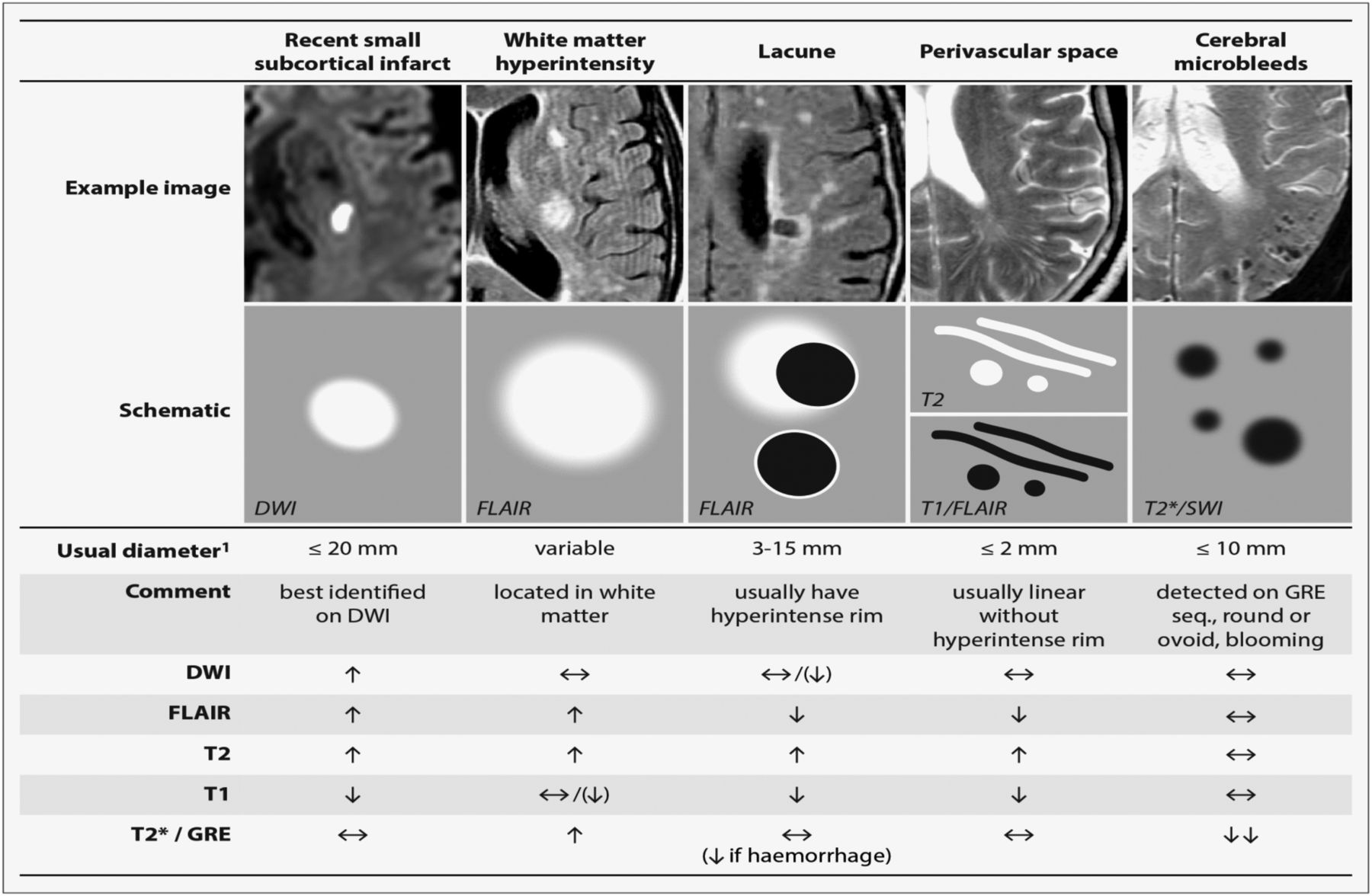
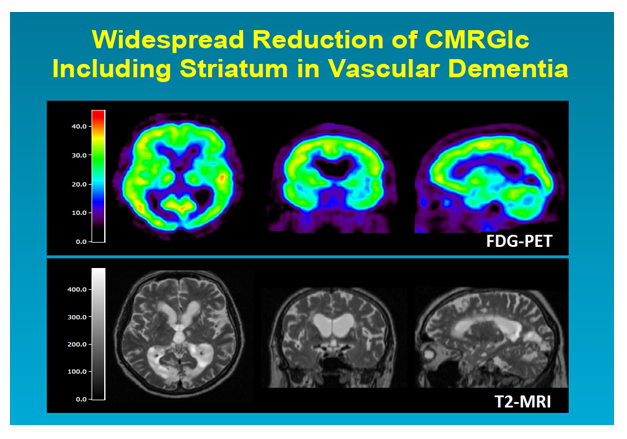
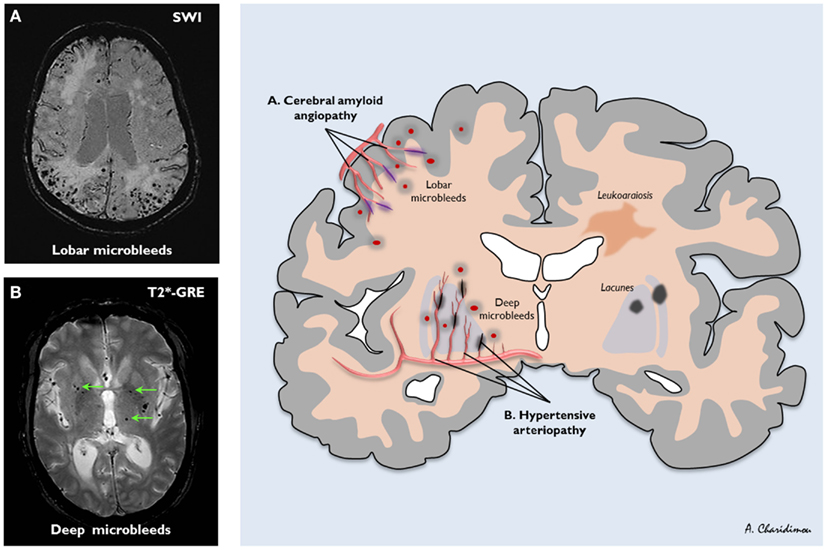
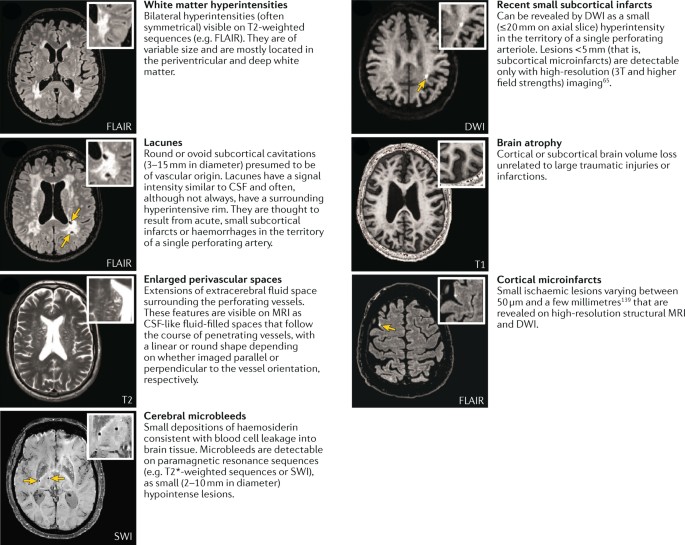
9 28 Most prevalent is arteriolosclerosis or simple SVD which is a concentric hyaline thickening of deep penetrating small arteries outer diameter vessel wall and depletion of vascular smooth. The term Chronic Small Vessel Disease CSVD refers to the physical changes caused by small vessel disease including thickening of the vessel walls disturbance of the blood-brain barrier and demyelination of the nerve sheaths. Cerebral small-vessel disease can be visualized on MRI studies as lacunar infarcts white matter lesions and cerebral microbleeds.
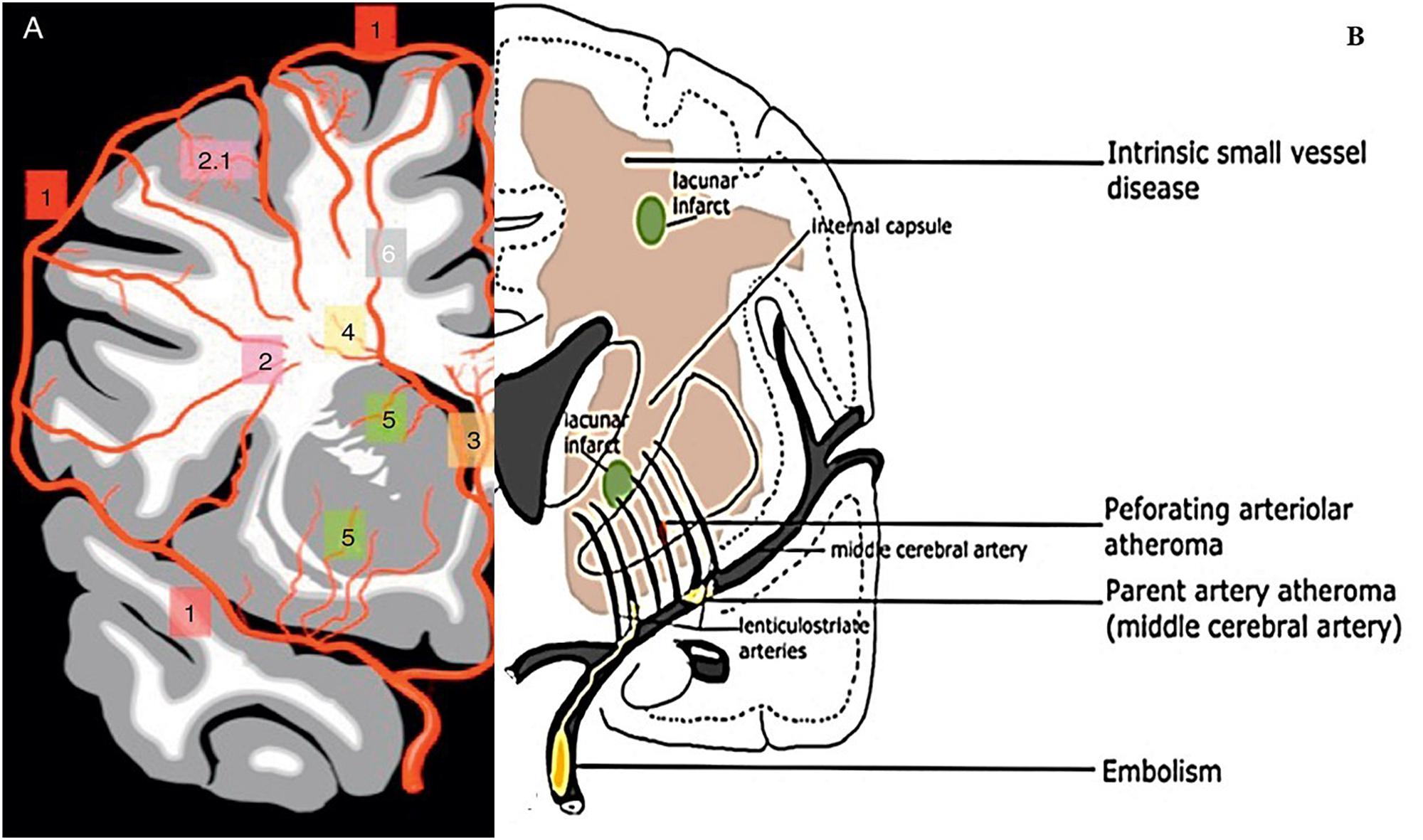
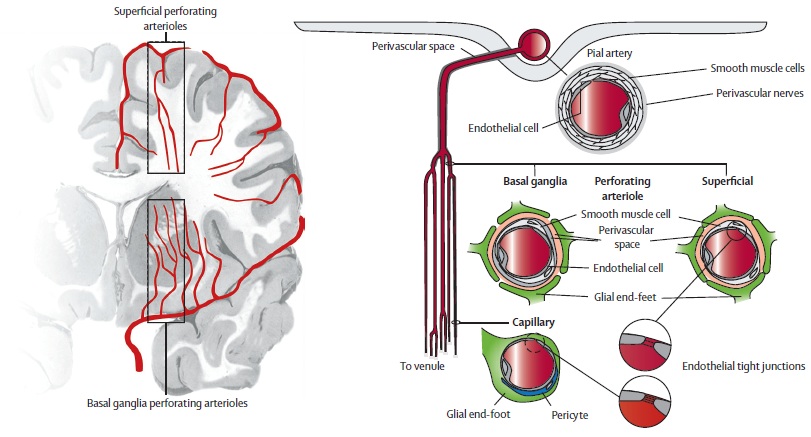
It is the most common incidental finding on brain scans especially in. Cerebral small vessel disease SVD is characterized by disease of the small perforating arteries which are defined as vessels with a diameter less than 50 μ m and all the vessels within the brain parenchyma plus the vessels with a diameter less than 500 μ m in the leptomeningeal space supplying the deep brain structures 1. Cerebral small vessel disease SVD is an umbrella term covering a variety of abnormalities related to small blood vessels in the brain.
Small vessel ischemia is a condition in which blood flow through small arteries and arterioles is restricted because of blockage or constriction of the vessels. Cerebral small vessel disease CSVD is the most common chronic and progressive vascular disease.
The term Chronic Small Vessel Disease CSVD refers to the physical changes caused by small vessel disease including thickening of the vessel walls disturbance of the blood-brain barrier and demyelination of the nerve sheaths.
Diminished or absent blood supply to the brain caused by obstruction thrombosis or embolism of an artery resulting in neurologic damage. It is associated with vascular risk factors such as hypertension atherosclerosis diabetes mellitus and atrial fibrillation 2 4. Cerebral small vessel disease SVD is an umbrella term covering a variety of abnormalities related to small blood vessels in the brain. Cerebral small-vessel disease can be visualized on MRI studies as lacunar infarcts white matter lesions and cerebral microbleeds. Cerebral SVD encompasses a range of vascular pathologies including arteriolosclerosis smallvessel atheroma and cerebral amyloid angiopathy as reviewed elsewhere. The changes affect arterioles capillaries and small veins supplying the white matter and deep structures of the brain. Small vessel ischemia is a condition in which blood flow through small arteries and arterioles is restricted because of blockage or constriction of the vessels. This is a slow process and is seen in diabetics hypertensives or in advanced aging. Microvascular ischemic disease describes conditions that affect the small blood vessels in the brain.
Small vessel ischemia is a condition in which blood flow through small arteries and arterioles is restricted because of blockage or constriction of the vessels. Because most brain tissue appears white on MRIs these abnormalities were historically referred to as white matter changes. Diminished or absent blood supply to the brain caused by obstruction thrombosis or embolism of an artery resulting in neurologic damage. This is a slow process and is seen in diabetics hypertensives or in advanced aging. Small vessel ischemia is a condition in which blood flow through small arteries and arterioles is restricted because of blockage or constriction of the vessels. These conditions include stroke cerebral hemorrhage and. Ischemic cerebral small-vessel disease accounts for a third of acute cerebral ischemic events and contributes to the development of cognitive decline and dementia.

































Posting Komentar untuk "Moderate Chronic Small Vessel Ischemic Disease"