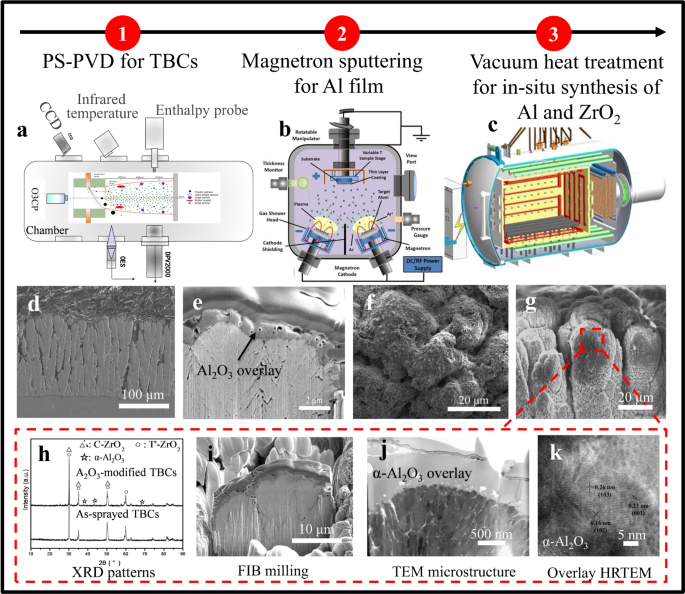
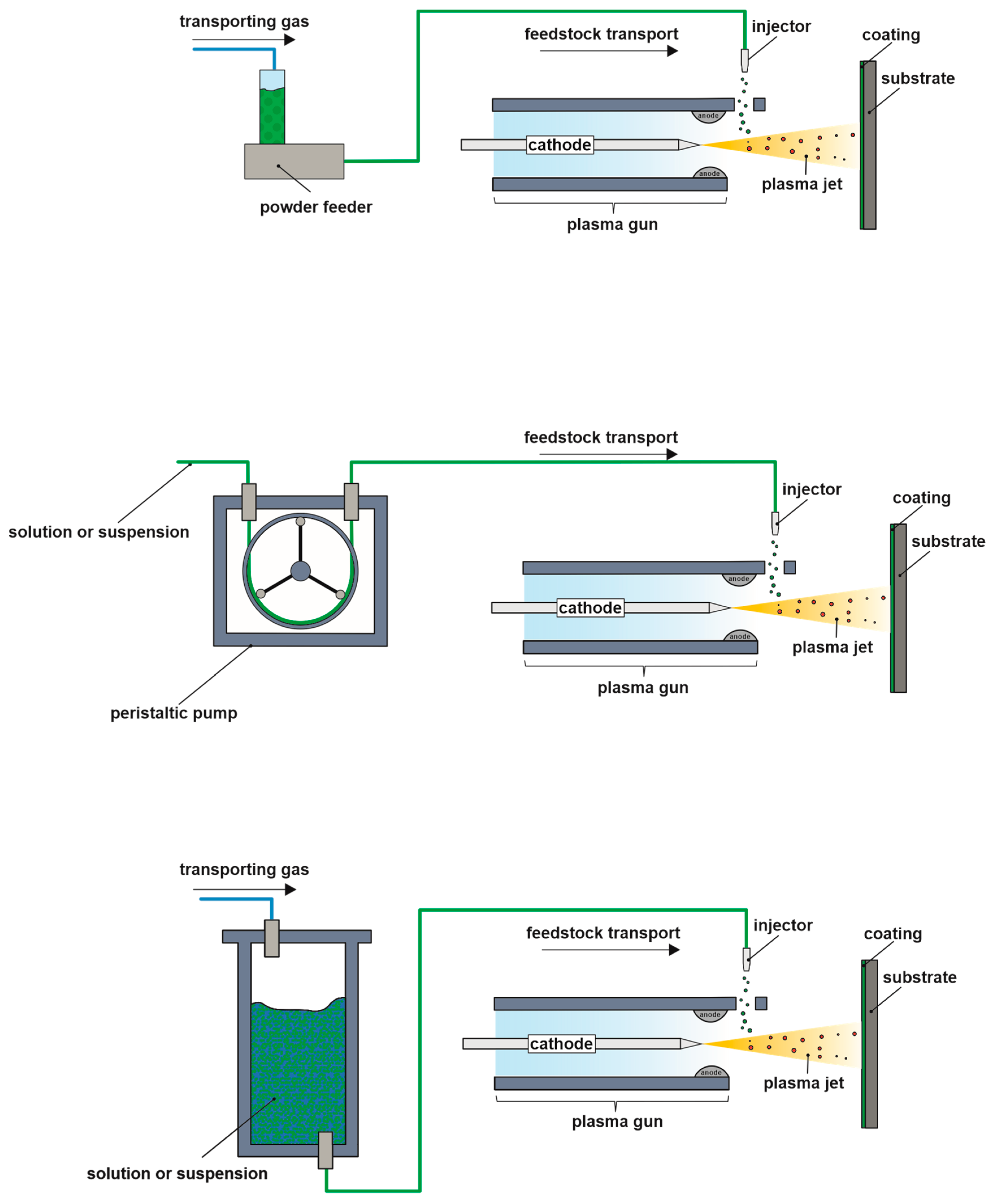
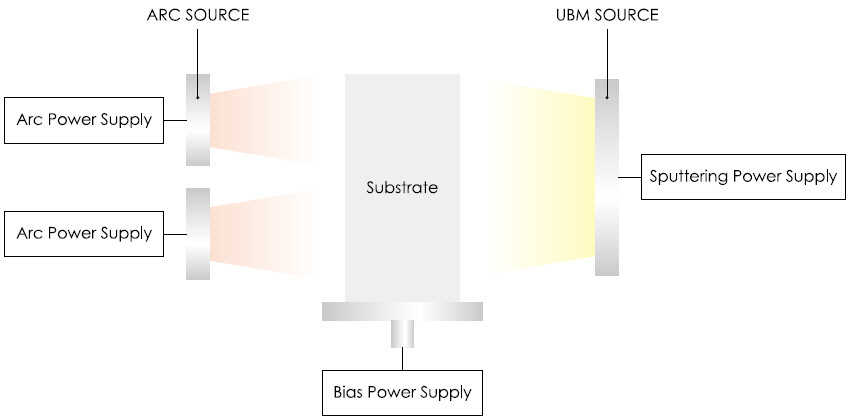
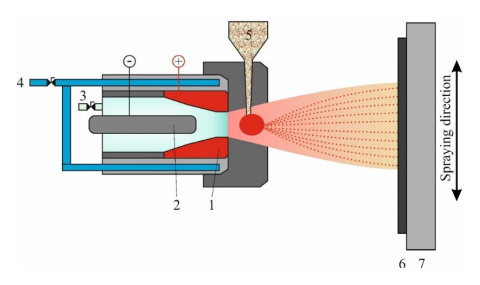
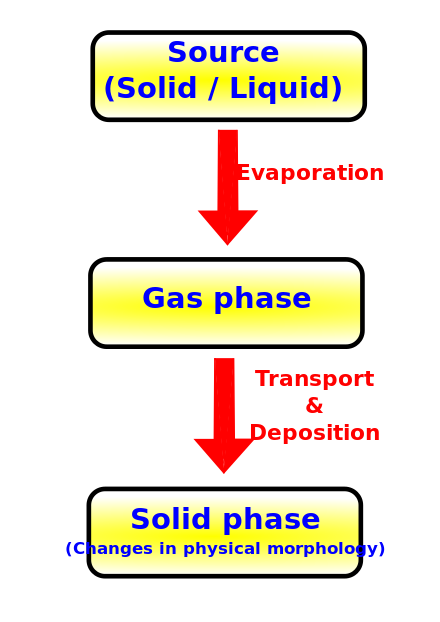
Plasma Spray Physical Vapor Deposition
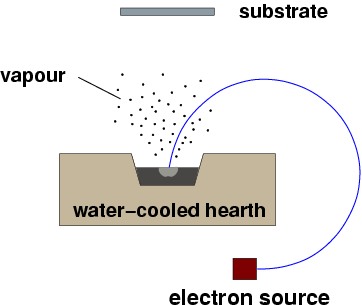
Plasma spray physical vapor deposition. The powders are fundamentally an aggregate of primary 20 nm particles which are composed of a crystalline Si core and SiO x shell structure. This technology is made possible by Glenns Plasma Spray Physical Vapor Deposition PS-PVD Facility. NASA Glenns Plasma Spray-Physical Vapor Deposition Rig uses a torch to create a high-powered plasma that vaporizes ceramic material and deposits it onto air.
After decades of years the concept of plasma spray-physical vapor deposition PS-PVD was emerged in 2010 2. Nanocomposite SiSiO x powders were produced by plasma spray physical vapor deposition PS-PVD at a material throughput of 480 g h-1. The key feature of.
An advanced processing technique Plasma Spray-Physical Vapor Deposition PS-PVD can deposit the layers needed for advanced turbine applications with tailorable compositions and microstructures. Ytterbium silicate coatings were deposited on SiCfSiC ceramics matrix composite CMC substrates by plasma spray-physical vapor deposition PS-PVD and the microstructures and phase constituents. And one of four in the entire world.
The technique further may include controlling by the computing device the plasma spray device to deposit an environmental barrier coating on a substrate in. Plasma sprayphysical vapor deposition PSPVD is a unique technology that enables highly tailorable functional films and coatings with various rare metal elements to be processed. Plasma Spray Physical Vapor Deposition PS-PVD is a relatively newer deposition that can reproduce similar structures.
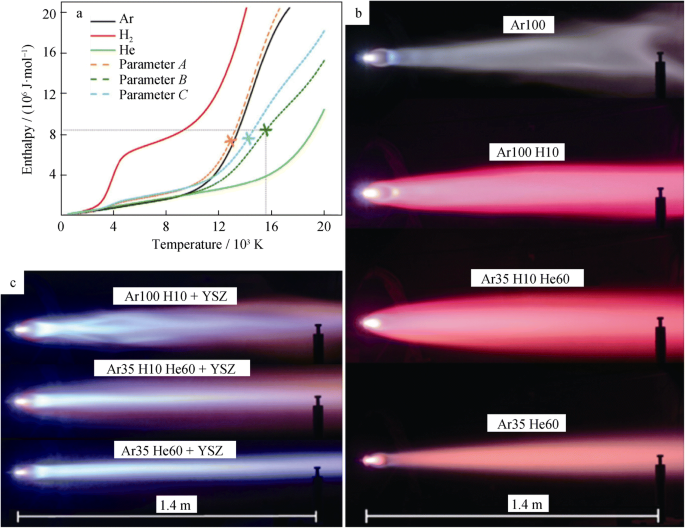
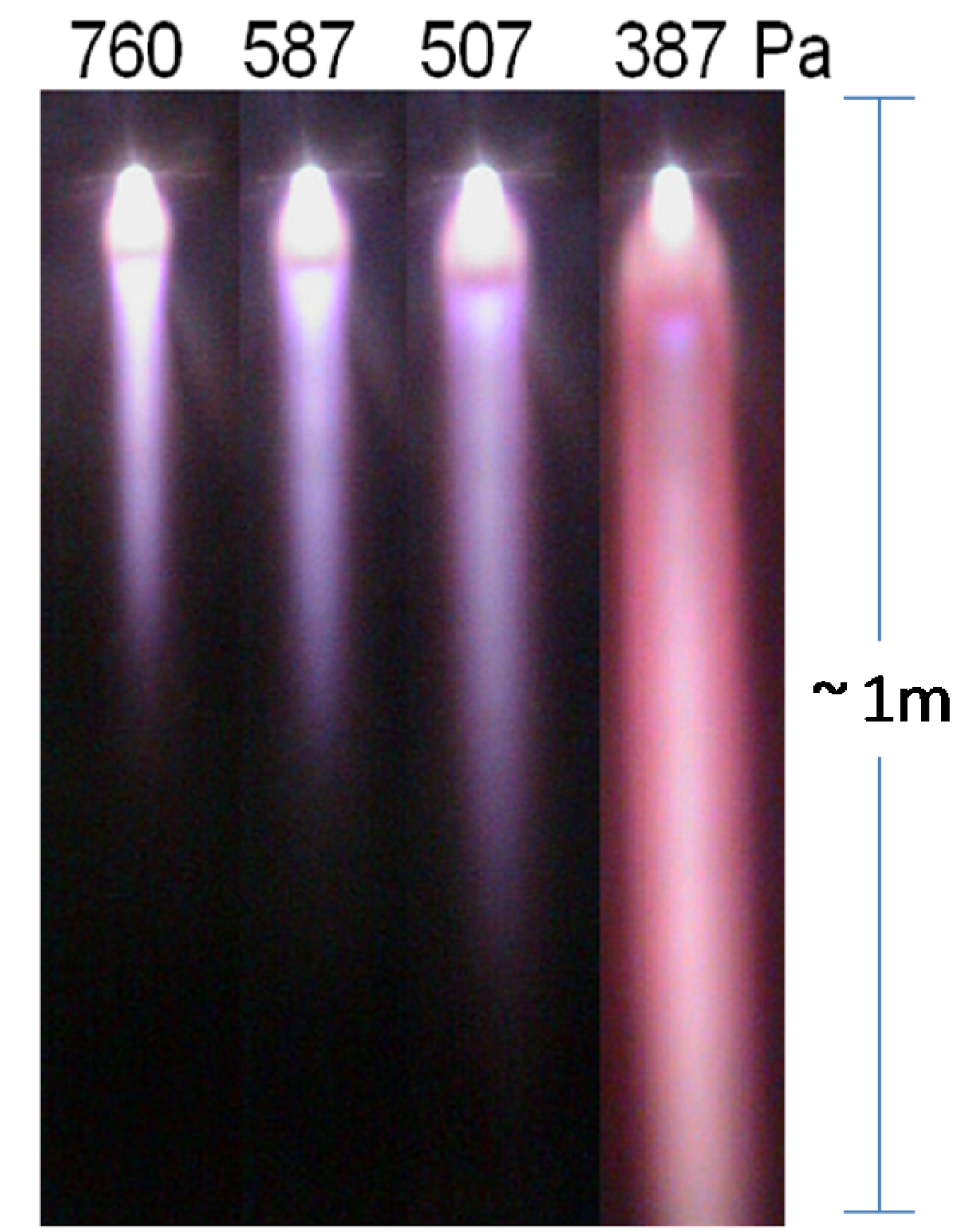
Even though it is a thermal spray process it can deposit coatings out of the vapor phase. The Plasma Spray Physical Vapor Deposition PS-PVD Coater was completed at Glenn in 2010. PS-PVD is featured with high power 180 kW and low vacuum 100 Pa.
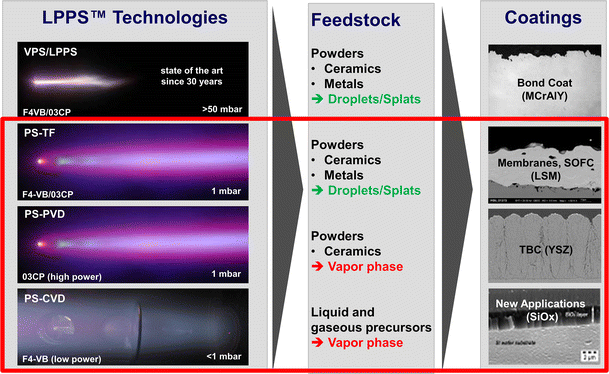
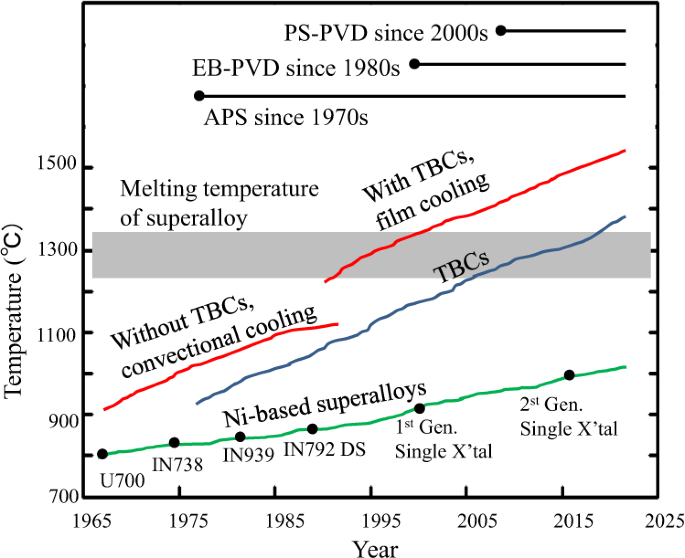
The low-pressure plasma spray-thin film LPPS-TF technology was first proposed by Sulzer Metco AG in 1998 1. A new processing technology known as Plasma Spray Physical Vapor Deposition PS-PVD has been developed in order to bridge the gap between conventional APS and PVD techniques to create unique microstructures34 The PS-PVD system at the NASA Glenn Research Center is one of only four systems currently available at this time. Created in collaboration with Sulzer Metco the PS-PVD rig is one of only two such facilities in the USA.
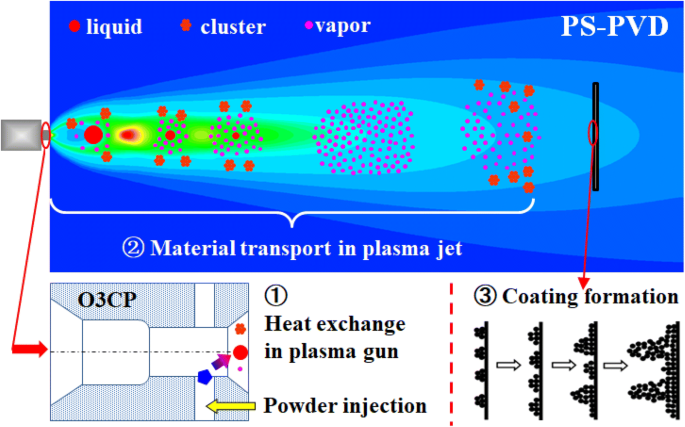
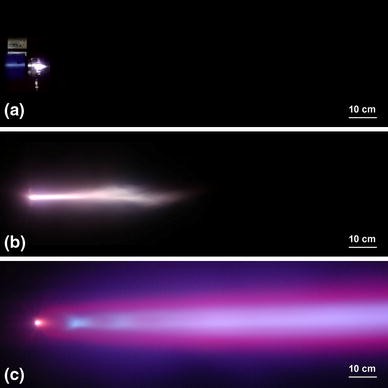
PS-PVD is a hybrid coating process that utilizes a thermal spray torch in a moderate vacuum 1 Torr for relatively fast coating deposition. This technology bridges the gap between conventional thermal spray and vapor deposition and provides a variety of coating microstructures composed of vapor liquid and solid deposition.
After decades of years the concept of plasma spray-physical vapor deposition PS-PVD was emerged in 2010 2.
The powders are fundamentally an aggregate of primary 20 nm particles which are composed of a crystalline Si core and SiO x shell structure. NASA Glenns Plasma Spray-Physical Vapor Deposition Rig uses a torch to create a high-powered plasma that vaporizes ceramic material and deposits it onto air. The key feature of. Ytterbium silicate coatings were deposited on SiCfSiC ceramics matrix composite CMC substrates by plasma spray-physical vapor deposition PS-PVD and the microstructures and phase constituents. Nanocomposite SiSiO x powders were produced by plasma spray physical vapor deposition PS-PVD at a material throughput of 480 g h-1. The powders are fundamentally an aggregate of primary 20 nm particles which are composed of a crystalline Si core and SiO x shell structure. PS-PVD is featured with high power 180 kW and low vacuum 100 Pa. PS-PVD is a hybrid coating process that utilizes a thermal spray torch in a moderate vacuum 1 Torr for relatively fast coating deposition. The low-pressure plasma spray-thin film LPPS-TF technology was first proposed by Sulzer Metco AG in 1998 1.
And one of four in the entire world. An advanced processing technique Plasma Spray-Physical Vapor Deposition PS-PVD can deposit the layers needed for advanced turbine applications with tailorable compositions and microstructures. After decades of years the concept of plasma spray-physical vapor deposition PS-PVD was emerged in 2010 2. Nanocomposite SiSiO x powders were produced by plasma spray physical vapor deposition PS-PVD at a material throughput of 480 g h-1. The use of Plasma Spray - Physical Vapor Deposition PS-PVD processing fills this gap and allows thin 10 microns single layers to be deposited and multilayer coatings of less than 100 microns to be generated with the flexibility to tailor microstructures by. Plasma Spray- Physical Vapor Deposition PS-PVD is an ideal process to deposit this material based on its capability to process coatings in a low pressure and low PO 2 environment. Xpowders were produced by plasma spray physical vapor deposition PS- PVD at a material throughput of 480gh1.


























Posting Komentar untuk "Plasma Spray Physical Vapor Deposition"